HISTORY
Establishment
1952
- Establishment
-
In 1952, founder Teruhiko Konishi started business as Konishi Chemical Industry.
After the end of the war, Mr. Teruhiko studied chemistry by himself, and Mr. and Mrs. Konishi manufactured chemicals such as artificial sweeteners in the backyard of their home.
In 1962, the company changed to a corporation and established Konishi Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. in Kozaika, Wakayama.
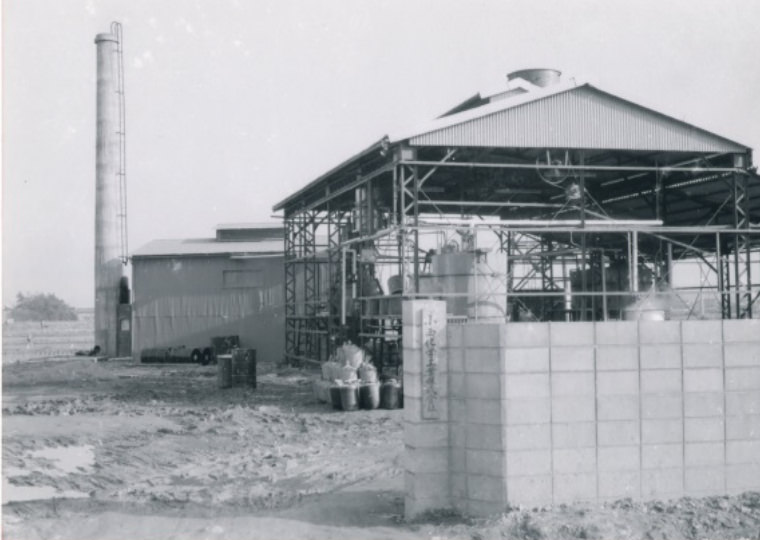

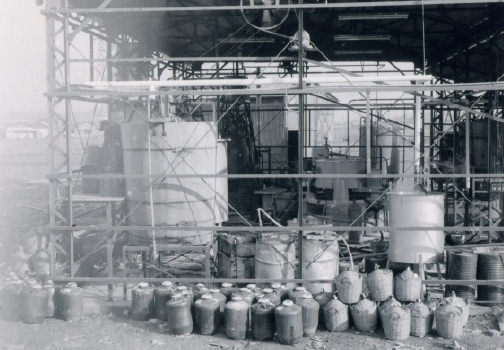
Konishi Chemical Kozaika in 1962
1962
- Konishi Chemical's sulfonation business
-
Konishi Chemical's sulfonation business began with the supply of sulfonated plating chemicals to plating chemical manufacturers. In the late 1960s, production of DHDPS (dihydroxydiphenyl sulfone) was started as a raw material for dyeing aids.
In 1972, the world's first high-purity DHDPS product was marketed and provided to Eastman Kodak Company, a major film manufacturer at that time, for yellow dye forming materials (yellow couplers). At that time, this high purity technology was necessary for color development of color films.
In addition, utilizing the sulfonation technology, Konishi Chemical proceeded with the development of many sulfonic acid derivatives and achieving higher purity, and sulfonation intermediate business became a pillar of their profit.
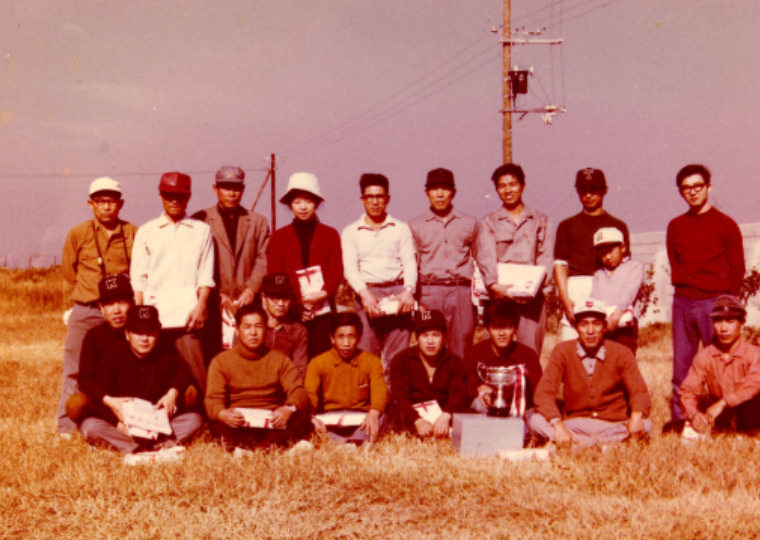 Member at the time 1968
Member at the time 1968
 DHDPS plant construction 1977
DHDPS plant construction 1977
Growth
1980
- DHDPS manufacturing technology license to ICI, UK
-
In the 1980s, the use of Konishi Chemical's DHDPS in yellow couplers was published in a British technical magazine, and ICI UK, the world's largest chemical manufacturer at the time, contacted Konishi Chemical to use DHDPS as a raw material for PES.
At that time, ICI was considering the global expansion of PES biz, but there was a concern about procuring basic raw materials from Konishi Chemical, one of the town factories in Wakayama. However, in-house development did not exceed the patents owned by Konishi Chemical.
As a result, ICI decided to purchase a DHDPS manufacturing technology license from Konishi Chemical, and the Konishi Chemical manufacturing DHDPS plant was put into operation in the ICI UK.
Wakayama's SME technology was recognized by the world's largest chemical manufacturer.
 ICI DHDPS plant started operation 1986
ICI DHDPS plant started operation 1986
 When ICI visited Wakayama 1982
When ICI visited Wakayama 1982
The DHDPS plant of Konishi process is in operation at ICI UK. A picture of a tape cut ceremony using a personal computer at the time. When Teruhiko Konishi pressed the button, scissors came out, and when the tape was cut, the Japanese flag came out.
Environmental Change
1995
- Crisis as an intermediate manufacturer
-
In the late 1990s, Chinese chemical companies began to emerge, and cheaper chemical products began to circulate.
Konishi Chemical’s products including DHDPS were also made in China, and their sales continued to decline.
As a result of these changes in the biz environment, Konishi Chemical decided to shift from the business centered on intermediates to the R & D business for functional materials.
From there, they worked on technology development through self-development of functional materials and contract manufacturing, and promoted research and development and strengthening of the production system.
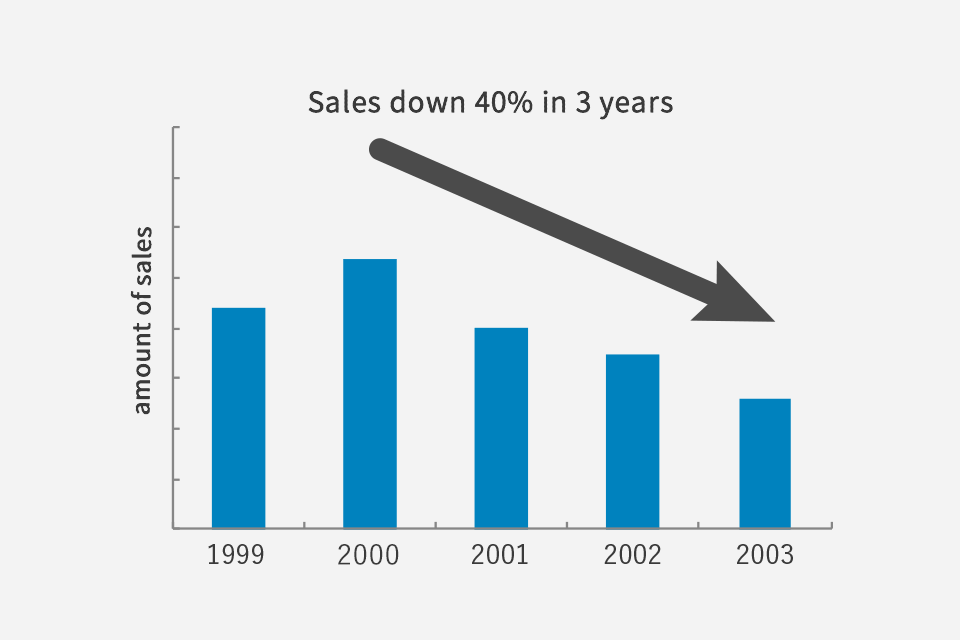 Sales trend from 1999 to 2003
Sales trend from 1999 to 2003
Conversion
2003
- From organic synthesis business to functional materials business
-
In 2003, Konishi Chemical started a contract manufacturing business for polyfunctional epoxy resins, which are thermosetting resins.
The product was later adopted by Boeing as an impregnation resin for carbon fiber composite material (CFRP). While achieving high quality control requirements for aircraft materials, they achieved it and started mass production as CFRP material for Boeing 787 aircraft.
In 2008, the company built the first development type multi-pilot plant to serve for a new business. This plant is designed to handle a wide range of manufacturing conditions for the production of functional materials, and is the starting point for many new businesses of Konishi Chemical.
In 2013, in response to the mass production system of Boeing 787, a new factory was established at Technoport Fukui in Fukui Prefecture as the second base for epoxy resin production, strengthening the production system.
 Development type multi-pilot plant
Development type multi-pilot plant
 Fukui Factory completed 2013
Fukui Factory completed 2013
 Boeing 787 aircraft
Boeing 787 aircraft
Challenging
2015
- Challenge to sustainable manufacturing
-
In 2015, China's environmental and safety regulations were tightened, and the supply chain of Chinese products became difficult to function, and the need for existing products such as DHDPS from Konishi Chemical increased.
Konishi Chemical has set up “sustainable manufacturing” and is aiming for a business structure that does not fluctuate with changes in the environment.
As one of the initiatives, the new DHDPS plant that started operation at the Fukui Plant in 2017 was designed as a smart factory that incorporates IoT technology such as operation control using tablet terminals and remote status monitoring using small cameras. The goal is sustainable supply. - Toward a chemical manufacturer aiming for the next generation
-
In 2018, the second development type multi-pilot plant was newly established in response to increasing demand in the development business. This plant will be a new production base for new businesses, such as polysilsesquioxane (PSQ) and functional sulfonated polymer (S-PES) born from technological change efforts.
In 2020, a new plant for DHDPS derivatives will be built at the Fukui Plant for thermal materials. The plant plans to promote instrumentation of IoT equipment.
 Fukui DHDPS new plant
Fukui DHDPS new plant
 Fukui Smart Factory
Fukui Smart Factory
 Wakayama second development type multi-pilot plant
Wakayama second development type multi-pilot plant
Because Konishi Chemical is aiming to be a company that is continuously needed,
they will keep on challenging for the future.

